What is osteochondrosis?
Causes of osteochondrosis and its complications
risk factors
- Longitudinal and transverse flat feet are present. Flat feet cause the arch of the foot to stop bouncing and impact forces are transmitted up the spine without softening. The intervertebral discs are under tremendous pressure and collapse rapidly;
- Overweight and obesity – no comment needed;
- Improper lifting and carrying of heavy objects causes uneven stress on the intervertebral discs. For example, if you carry a bag of potatoes on your shoulders, the powerful load will rest on one edge of the disc and may be too large;
- Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle. As mentioned above, the greatest pressure on the intervertebral disc is when sitting, because people never sit upright, but always "slightly" curved;
- Chronic injuries, slipping on ice, strenuous lifting, exposure to martial arts, wearing heavy hats, hitting your head on low ceilings, heavy clothing, carrying heavy bags in your hands.
General symptoms
Pain: Muscle and nerve root pain
Radicular pain: compressive radiculopathy
Muscle pain: myofascial ankylosis
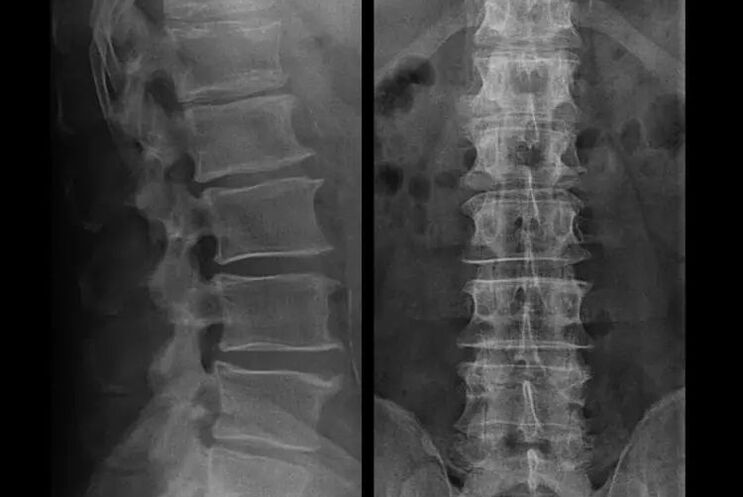
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
Treatment of complications of osteochondrosis
- If you have symptoms of narrowing of the intervertebral disc height, you need to exercise correctly, do not gain weight, and avoid protrusions and muscle pain;
- If there is already a herniation, care needs to be taken not to let it rupture the annulus fibrosus, that is, not to convert the herniation into a hernia, and to avoid the occurrence of multi-level herniations;
- If you have a hernia, then you need to monitor it dynamically, undergo regular MRI scans, avoid increasing its size, or undergo modern minimally invasive surgical treatment, since all conservative methods of treating the exacerbation of osteochondrosis without exceptionThe hernia remains in place and eliminates only temporary symptoms: inflammation, pain, shooting and muscle spasms.
What should I do when my condition worsens?
- Complete elimination of physical activity;
- Sleep on a firm mattress (orthopedic mattress or firm sofa) to eliminate back sagging;
- It is recommended to wear a semi-rigid corset to prevent sudden movements and "twisting";
- You should place a massage pillow with plastic needles on your lower back, or use a Lyapko massager. It needs to be maintained for 30-40 minutes, 2-3 times a day;
- Afterward, an ointment containing NSAIDs, bee venom, or snake venom can be rubbed into the lower back;
- After wiping, the next day you can wrap your waist with a dry heat wrap, such as a band made of dog hair.
- To reduce muscle and spinal swelling, a salt-free diet and limited fluid intake are recommended. You can even take a mild potassium-sparing diuretic;
- In the acute stage of lumbar osteochondrosis, short-term treatment can be carried out through intramuscular "injection" of NSAIDs and muscle relaxants: 1. 5ml intramuscular injection daily for 3 consecutive days, or 1ml intramuscular injection for 5 consecutive days. This will help relieve nerve tissue swelling, eliminate inflammation, and normalize muscle tone;
- In the subacute phase, after the maximum pain has been overcome, no more "injections" should be given, attention should be paid to restorative drugs, such as modern drugs of the "B" group. They can effectively restore damaged sensitivity and reduce numbness and paresthesia.
About Shants collar
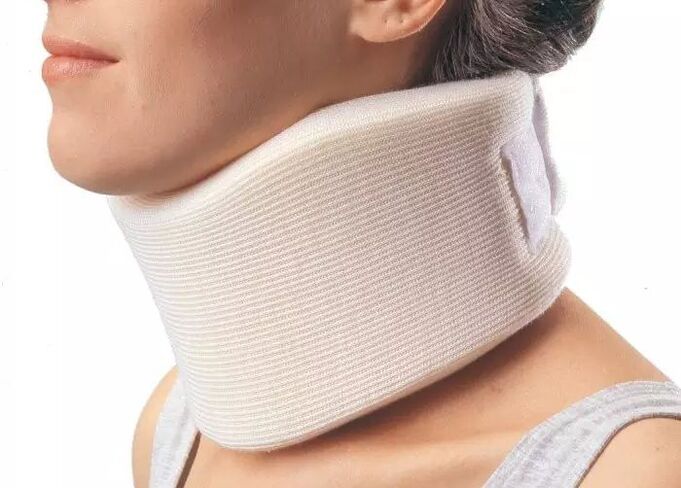
- Acute pain and stiffness in the neck that spreads to the head;
- If you do physical work while you are healthy, there is a risk of "straining" your neck and aggravating the condition. For example, when you're lying under a car to work on your car, or when you need to reach out and assume an awkward position to wash your windows.
Surgical treatment or conservative treatment?
Prevention of osteochondrosis and its complications
- Avoid hypothermia, especially in fall and spring, and in winter and fall;
- Do not lift heavy objects, only carry heavy objects in the backpack with your back straight;
- Drink plenty of clean water;
- Don’t get fat, your weight should correspond to your height;
- Treat flat feet (if you have them);
- engage in regular physical exercise;
- Engage in exercise that relieves stress on the back (swimming);
- Quit bad habits;
- Alternate mental stress with physical activity. After every hour and a half of mental work, it is recommended to change the type of activity to physical work;
- You can regularly have at least one lumbar X-ray (two projections) or MRI to see if the hernia, if any, is progressing;